Application Note: Considerations for Cleared Tissue Imaging with Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy in Neuroscience Research
Explore the Advantages of Light-Sheet Microscopy for Neuroscience Research
Conventional neuroimaging methods often rely on destructive and technically-complex sample preparation and optical reconstruction techniques to overcome the limitations in penetration depth caused by light-scattering and light-absorbing components in biological tissue samples.
Conversely, Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) can image large, optically cleared (ex vivo) samples and — when combined with tissue clearing for non-transparent samples — can penetrate many millimeters through a specimen, unrestricted by scattering and absorption, enabling the acquisition of whole tissues, brains, and even organisms.
This brief includes a case study demonstrating mouse brain imaging with LSFM cleared by CLARITY (Clear Lipid-exchanged Acrylamide-hybridized Rigid Imaging / Immunostaining / in situ-hybridization-compatible Tissue hYdrogel).
Contents include:
- The unique capabilities of light-sheet fluorescence microscopy for neuronal to whole-brain imaging
- The advantages and limitations of light-sheet fluorescence microscopy in neuroscience applications
- Important considerations for neuroscientists adopting LSFM techniques for cleared sample imaging
- The innovative neuroscience research LSFM now supports
KEYWORDS: Neuroscience Research; Case Study; Light-Sheet Microscopy; Cleared Sample Imaging; Tissue Clearing; CLARITY
Introduction
A major goal in the field of neuroscience is to understand the connectivity of the brain across scales, from individual synaptic connections to whole organism connectomics. Visualizing the whole brain often requires imaging at depths that are not supported by conventional imaging methods, such as laser scanning confocal microscopy. In recent years, lightsheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) has emerged as an imaging technique capable of addressing a wide variety of applications in neuroscience due to its faster acquisition speed and larger imaging depth compared to confocal microscopy. Although early implementations of LSFM were optimized around imaging developmental processes in typical model organisms, technological advances in optics have allowed researchers to extend this technique to much larger samples, such as an entire mouse brain. Combined with emerging tissue clearing techniques, researchers are now able to investigate intact tissues, organs, and even entire organisms with subcellular resolution using light microscopy methods. The versatility of LSFM for neuroscience research has contributed to its rapid adoption and increasing popularity in the scientific community. However, there are multiple important factors one must consider when moving from standard imaging techniques to LSFM. This application note discusses the reasons why LSFM and clearing techniques are particularly useful for neuroscience research, important considerations for neuroscientists adopting this technology, and application examples of LSFM for cleared sample imaging.
Introduction to Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy and Tissue Clearing in Neuroscience
Principles, Advantages, and Limitations of Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging technology is an indispensable tool for neuroscience research. Currently, there are many imaging approaches utilized by neuroscientists to address different research questions, ranging from fMRI to confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM).1 CLSM is a workhorse technique that has been used broadly in neuroscience, including in the acquisition of high-resolution images of neurons, astrocytes, and blood vessels.2 While CLSM has the advantage of imaging labeled targets at high resolution, it is limited in acquisition speed and its ability to image deep into samples and thus cannot be used to image thick samples, such as a whole mouse brain. Multiphoton excitation fluorescence microscopy (MPFM) methods have been developed to image deeper into tissue, achieving depths of around 1 mm in the mouse brain.3 However, due to the sequential scanning nature of MPFM, this method is still much slower than the more recently developed LSFM technology. In contrast to CLSM and MPFM, LSFM achieves optical sectioning by illuminating a single plane of interest with a sheet of light and using a camera focused on that very plane for image collection.
Compared to laser scanning methods, the optical concept of LSFM enables faster and gentler imaging. The acquisition speed of an LSFM is mostly limited by the readout rate of the camera, for example, an LSMF equipped with a state-of-the-art scientific CMOS (sCMOS) camera can be operated at approximately 50 frames per second (fps) with a spatial sampling of 2048 x 2048 pixels per frame. The acquisition speed of a laser scanning system, on the other hand, is mostly limited by the scanning speed of the galvanometer scanner. For example, a CLSM equipped with a resonant 16 kHz scanner can be operated at approximately 5 fps with the same spatial sampling. Thus, imaging an entire mouse brain of 10 x 10 x 10 mm3 at a 3D sampling of 1 x 1 x 2 μm3 takes about 6 hours on an LSFM and 2.5 days on a CLSM or MPFM. Photobleaching of fluorophores is drastically reduced in an LSFM because only a single plane is illuminated at a time and the laser illumination time for each fluorophore is orders of magnitude shorter for laser scanning methods. The shorter illumination time requires much higher illumination intensities to obtain the same number of fluorescence photons such that laser scanning methods drive fluorophores much more likely into nonfluorescent states than LSFM, i.e., photobleaching. Additionally, the imaging depth capabilities of LSFM can be advantageous compared to CLSM, as demonstrated in a study in which both methods were used to image the diffusion of small drug molecules within a tumor spheroid.4 It was shown that confocal microscopy could not accurately image the molecular diffusion within the tissue beyond 100 μm in depth, while LSFM was able to image fluorescence down to the core of the spheroid, which was 1 mm in depth. In summary, with LSFM, the fast and gentle imaging of thick samples, whole tissues, and organs with high lateral and depth resolution is possible while reducing the typical limitations of light microscopy methods. LSFM has gained popularity in recent years and was even named the Nature Method of The Year in 2014.5
LSFM was conceptualized over 100 years ago,6 however its potential for life science research was not realized until recently. The earliest implementation of modern-day light-sheet microscopy was orthogonal-plane fluorescence optical sectioning (OPFOS). In OPFOS, the sample was illuminated by a sheet of laser light created with a cylindrical lens and orthogonal detection with a CCD camera.7 A decade later, a landmark paper introduced selective plane illumination microscopy (SPIM), which uniquely utilizes separate illumination and detection objectives, oriented orthogonally to one another, combined with sample rotation around a vertical axis for fast and three-dimensional image acquisition.8 SPIM has been used in research across several life science disciplines, originating with applications in developmental biology,8, 9 and meanwhile extending to cell biology,10, 11 cancer biology,12 medicine,4 and neuroscience.13 To date, SPIM/LSFM technology has been applied to many neuroscience research questions including, but not limited to, the mapping of olfactory responses in the mouse vomeronasal organ,14 as well as the imaging of neuronal calcium signaling at the synapse in both a mammalian brain and the entire brain of the zebrafish larvae.15, 16 There have been significant advancements in LSFM technology over recent years—such as further improvements to objective lens design, imaging speeds, and spatial resolution—that make it well-suited for applications in cleared tissue imaging in neuroscience,17 which is important for questions that require imaging of thick and large tissues, such as the brain.
The Importance of Clearing Brain Samples for Imaging
Biological tissues are inherently three-dimensional. Due to the properties of light, it is extremely difficult to perform imaging deep into three-dimensional tissue. Biological tissue is composed of lipids, cytoskeleton, collagen, elastin, and other light-scattering and light-absorbing components that restrict the ability of standard fluorescence microscopy techniques from imaging farther than about 200 μm into tissue.18 This is limiting for neuroscience research, as many questions require a deep look into a brain slice or whole brain that is much thicker than 200 μm. Due to limitations in the penetration depth for conventional microscopes, most techniques for interrogating three-dimensional tissue have relied on methods like tissue sectioning. Besides the drawback of physically destroying the tissue, tissue sectioning makes optical reconstruction difficult as it requires lining up the various sections to stitch together a holistic view of the sample. Although difficult, various techniques, such as electron microscopy and array tomography, have been successful.19, 20 This approach is technically challenging due to loss or distortion of individual sections that become torn, folded, compressed, or stretched. With imperfect sections, the final volumetric reconstruction can be unsatisfactory.
As a solution to these challenges caused by physical tissue sectioning, LSFM has been adapted to image large, optically cleared (ex vivo) samples of mouse brains by implementing long working distance objectives, creative sample mounting, and larger imaging chambers.21 If tissue is not transparent by default, it must be rendered transparent through tissue clearing. Tissue clearing modifies the optical properties of usually opaque samples to render them transparent while keeping their three-dimensional structure intact. With tissue clearing, the main goal is to remove scattering and absorbing components and to homogenize the refractive index (RI) of the sample. Once the tissue has been cleared, light can travel many millimeters through a specimen, unrestricted by scattering and absorption, making these samples ideal for optical interrogation with LSFM.
In the last decade, there has been a surge in development of tissue clearing techniques and their applications to neuroscience research have been reviewed elsewhere.22 Despite the diversity of clearing techniques, they can be sorted into three main categories: solvent-based, aqueous based, and employing hydrogel embedding.23, 24 Choosing the best clearing technique for a specific sample depends on many factors, including the type of tissue, the required fluorescent labelling method, and the sample size. For example, solvent-based clearing methods dehydrate and shrink the sample, tend to have a very high RI, short clearing times, and work best with immunofluorescence labelling methods.25 Aqueous-based clearing methods work for small samples, have limited clearing capacity, take a long time to clear, and work with both immunofluorescence and genetically encoded fluorophores.26 Finally, hydrogel-based clearing methods entail a long, complex protocol but have a high clearing capacity due to delipidation, work well with immunofluorescence and genetically encoded fluorophores, and result in slightly expanded tissues.27 In general, there is no single clearing method that will work for all tissue types, sizes, or experiments.
Considerations for Cleared Sample Imaging with LSFM
The combination of LSFM imaging with cleared samples opens new frontiers in neuroscience research, enabling the acquisition of whole tissues, brains, and even organisms. However, there are several important factors to consider prior to exploring how cleared-sample imaging with LSFM can fit into a research question. With LSFM, choosing the right microscope on which to image the tissue is as important as the choice of the right clearing method itself. This section discusses microscope-dependent considerations, including sample size and mounting, objective lenses, and geometric arrangement of lenses.
Sample Size and Mounting
One of the most important considerations for cleared tissue imaging with LSFM is the sample size. Firstly, one must ensure that the sample will fit inside the microscopy imaging chamber. In neuroscience, the size of a sample could range from a tissue section that is several millimeters thick to an entire mouse brain that is 1 cm3. The maximum size of the sample that the microscope can accommodate will ultimately determine which system will work best. Different LSFM systems have different sample mounting apparatuses ranging from mounting on slides, hanging the sample, drawing the sample up into a capillary, and mounting in a cuvette. If the goal is imaging the entire mouse brain, a large cuvette sample mounting system is a simple straightforward choice. However, mounting the mouse brain by gluing it to various sample holders might yield more experimental flexibility, such as isotropic resolution through multiangle acquisition.
Detection Objective Lens
Another major consideration for cleared tissue imaging is the detection objective lens on the microscope, specifically its working distance, numerical aperture, and compatibility with different RI-matching media. Large, cleared samples, such as whole mouse brains, require long working distance objectives to be able to image entire samples. For optimal imaging conditions, one must ensure that the objective working distance is long enough to image through the sample without physically colliding into the lens. If the sample is too big to image all the way through, some light-sheet systems can rotate the sample to image it from the opposite side, allowing the entire volume to be imaged.
The resolution of the detection objective is another major factor to consider when designing LSFM experiments to investigate cleared samples. Unlike CLSMs, which have a plethora of different objective lens options, LSFMs typically have only a few detection objective options, mainly because of the much larger working distance required for imaging through thick samples. Air objectives have been used traditionally for such applications, as they do provide the required long working distance. However, these objectives typically feature a low numerical aperture and, therefore, low resolving power. Recently, objective manufacturers have created immersion lenses with high numerical aperture and multi-millimeter working distances. These new lenses allow researchers to image cleared samples at subcellular resolution millimeters deep into the sample, and therefore to investigate intact tissue in ways that were not possible before.
Finally, it is important to make sure that the clearing method is compatible with the detection objective. Specifically, one needs to take into consideration the composition of the RI match media and the overall RI of the sample. Organic solvent clearing methods, such as benzyl alcohol/benzyl benzoate (BABB) and immunolabeling-enabled imaging of solvent-cleared organs (iDISCO), use chemicals that are particularly harsh and that can dissolve the glue holding the front lenses on immersion objectives in place. An easy solution is to utilize air objectives in combination with cuvette-based mounting. However, more objective manufactures have recently created various adhesives for immersion lenses that are resistant to these solvents. Since immersion lenses for cleared tissue imaging have varying ranges of the RIs that they can effectively image, it is best to ensure that the resulting RI of the cleared sample is aligned with the capability of the lens. Additionally, it is important to match the RI of the sample to the RI of the imaging media to reduce image distortion.
Geometrical Arrangement of Objective Lenses
Most LSFMs for cleared tissue imaging utilize separate detection and illumination lenses that are oriented in various geometries. One popular geometry for imaging expanded samples and cleared brain slices uses two upright objectives. In this orientation, the objectives are aligned orthogonally to each other, such that one objective delivers excitation illumination light, and the other is used for detection. These objectives are identical, and their functions can be swapped so that the excitation objective becomes the detection objective and vice versa. These datasets can be merged and processed to achieve a final image with the same resolution in X, Y and Z, also known as isotropic resolution. Upright, two-objective geometries enable imaging of a variety of sample types, sizes, and preparations, including cleared organs and cleared tissue slices. In a three-objective geometry, where two are used for illumination and one is used for detection, the detection objectives can be orientated from above, below, or horizontally. Finally, a four-objective geometry can be achieved with two illumination and two detection objectives placed in a horizontal fashion. This configuration supports fast, three-dimensional imaging of a sample, and because there is no “back side” of the sample, the entire volume can be effectively imaged without a single rotation. This is beneficial when imaging soft and delicate large, cleared samples, as it minimizes any chance of disturbance from rotation. The flexibility of objective lens geometries with LSFM enables a greater variety of experimental conditions in neuroscience. The most common lens geometries for large, cleared specimens have been highlighted here, however more subsets of possible geometries can be found in the work of Kromm, et. al.28
In Practice: Cleared, Whole Brain Imaging with LSFM
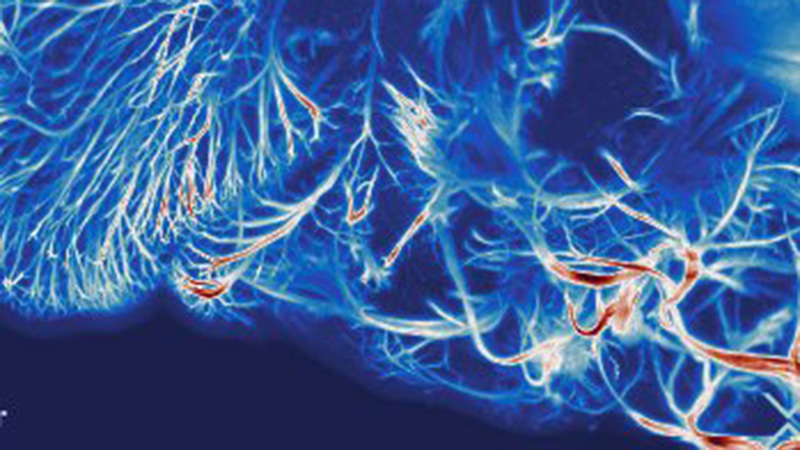
LSFM provides the depth, speed, and resolution needed to image cleared whole brain samples. Figure 1 shows an example of mouse brain imaging with LSFM cleared by CLARITY.29
Case Study
Imaging Pyramidal Neurons in Whole Mouse Brain Cleared with CLARITY
When combining tissue clearing with LSFM, it is possible to image specific structures within a thick brain slice. In this case study, a transgenic mouse brain was imaged. The depth of imaging was made possible by using the hydrogel-based clearing technique CLARITY (Clear Lipid-exchanged Acrylamide-hybridized Rigid Imaging / Immunostaining / in situ-hybridization-compatible Tissue hYdrogel). A Thy1-YFP mouse was used and the pyramidal neurons in the sample have been visualized in the global context of the entire brain (see Figure 2).
Large, cleared samples, such as the mouse brain, do often exceed the size of the field of view (FOV) of the microscope. To compensate the limited FOV, the sample is imaged in a grid-like fashion called tiling, where the stacks are imaged sequentially in a neighboring fashion, with each stack having some lateral overlap with neighboring stacks. This way the large sample can be imaged in high resolution. Consequently, the montage-like data has to go through a post-processing process called stitching, where neighboring tiles (the single stacks) are registered to each other and then fused together. The resulting fused dataset is a little bit smaller than the sum of the individual tiles due to the overlapping regions, but as the number of tiles can reach tens or even hundreds for large samples at high resolution, the amount of data can easily reach the TB regime, such that even with powerful workstations used for processing, smart algorithms have to be applied.30
Discussion
Light-sheet microscopy is an emerging and powerful tool for the advancement of neuroscience research. The main advantage of light-sheet microscopy for the neuroscientist is the ability to quickly and gently image physically intact, large, specifically labelled samples with high resolution. Sample clearing for imaging is particularly relevant to the neuroscientist investigating thick, large samples, such as brain slices or whole mouse brains. For deep optical imaging in biological tissue, clearing is often necessary to render it transparent enough to achieve the desired imaging depth. Tissue clearing methods are less physically damaging than tissue slicing, and do not require the effort of making the slice images fit together to achieve a picture of the whole brain. There are several factors to take into consideration when choosing a clearing method for your sample of interest, including size, labelling method, and tissue type. When cleared samples are imaged with LSFM, the user can achieve an unprecedented combination of imaging depth, speed, and isotropic resolution, especially when compared to more conventional optical imaging methods. In addition to choosing the best tissue clearing method, there are many considerations for which LSFM setup is best, including sample size and mounting method as well as choice and geometrical arrangement of objective lenses. Understanding which options for both tissue clearing and LSFM setup are best suited for the research question at hand is key to obtaining optimal image data.
Currently, LSFM technologies are available and optimized to image an entire mouse brain with the size of about 1 cm3 and beyond. Going forward, modifications to objective lens setups and sample mounting apparatuses may be necessary to image large brain sections of other model organisms, such as ferrets or monkeys. A future frontier in light-sheet microscopy will be multimodal imaging, the ability to integrate LSFM with other imaging approaches. For example, correlating the high-resolution, cleared tissue imaging capability of LSFM with the live, non-invasive visualization of MRI will enable further advancements in neuroscience research. Improvements in labeling strategies will also contribute to the evolution of this approach. Additionally, technological advances in image processing and analysis software, such as faster stitching of many tiles for a dataset, will support more streamlined data acquisition and analysis.
References
- Ganesana, M., Lee, S. T., Wang, Y., and Venton, B. J. (2016). Analytical techniques in neuroscience: Recent advances in imaging, separation, and electrochemical methods. Analytical Chemistry 89(1): 314–41. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04278.
- Pérez-Alvarez, A., Araque, A., and Martín, E. D. (2013). Confocal microscopy for Astrocyte in vivo imaging: Recycle and Reuse in Microscopy. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00051.
- Horton, N. G., Wang, K., Kobat, D., Clark, C. G., Wise, F. W., Schaffer, C. B., and Xu, C. (2013). In vivo three-photon microscopy of subcortical structures within an intact mouse brain. Nature Photonics 7(3): 205–09. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.336.
- Lazzari, G., Vinciguerra, D., Balasso, A., Nicolas, V., Goudin, N., Garfa-Traore, M., Fehér, A., Dinnyés, A., Nicolas, J., Couvreur, P., and Mura, S. (2019). Light sheet fluorescence microscopy versus confocal microscopy: In Quest of a suitable tool to assess drug and nanomedicine penetration into multicellular tumor spheroids. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 142: 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.06.019.
- Method of the Year 2014. Nat Methods 12, 1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.325251.
- Siedentopf, H., and Zsigmondy, R. (1902). Uber Sichtbarmachung und Größenbestimmung Ultramikoskopischer Teilchen, MIT besonderer Anwendung auf Goldrubingläser. Annalen Der Physik 315(1): 139. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.19023150102.
- Voie, A. H., Burns, D. H., and Spelman, F. A. (1993). Orthogonal-plane fluorescence optical sectioning: Three-dimensional imaging of macroscopic biological specimens. Journal of Microscopy 170(3): 229–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03346.x. 7
- Huisken, J., Swoger, J., Del Bene, F., Wittbrodt, J., and Stelzer, E. H. (2004). Optical sectioning deep inside live embryos by Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy. Science 305(5686): 1007–09. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1100035
- Krzic U., Gunther S., Saunders T. E., Streichan S. J., and Hufnagel L.(2012). Multiview light-sheet microscope for rapid in toto imaging. Nat Methods 3;9(7): 730-33. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2064. PMID: 22660739.
- Capoulade J., Wachsmuth M., Hufnagel L., and Knop M. (2011). Quantitative fluorescence imaging of protein diffusion and interaction in living cells. Nat Biotechnol29(9): 835-39. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1928. PMID: 21822256.
- Chen B. C., Legant W. R., Wang K., Shao L., Milkie D. E., Davidson M. W., Janetopoulos C., Wu X. S., Hammer J. A., Liu Z., English B. P., Mimori-Kiyosue Y., Romero D. P., Ritter A. T., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Fritz-Laylin L., Mullins R. D., Mitchell D. M., Bembenek J. N., Reymann A. C., Böhme R., Grill S. W., Wang J. T., Seydoux G., Tulu U. S., Kiehart D. P., and Betzig E. (2014). Lattice light-sheet microscopy: Imaging molecules to embryos at high spatiotemporal resolution. Science 346(6208):1257998. doi: 10.1126/science.1257998. Epub 2014 Oct 23. PMID: 25342811; PMCID: PMC4336192.
- Alladin, A., Chaible, L., Garcia del Valle, L., Sabine, R., Loeschinger, M., Wachsmuth, M., Hériché, J.-K., Tischer, C., and Jechlinger, M. (2020). Tracking cells in epithelial acini by light sheet microscopy reveals proximity effects in breast cancer initiation. ELife 9. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.54066.
- de Medeiros, G., Kromm, D., Balazs, B., et al. (2020).Cell and tissue manipulation with ultrashort infrared laser pulses in light-sheet microscopy. Sci Rep 10: 1942. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54349-x.
- Keller, P., Ahrens, M. and Freeman, J. (2015)Light-sheet imaging for systems neuroscience. Nat Methods 12: 27–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3214.
- Ahrens, M., Orger, M., Robson, D., et al. (2013). Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light-sheet microscopy. Nat Methods 10: 413–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2434.
- Yang, Z., Haslehurst, P., Scott, S., et al. (2016)A compact light-sheet microscope for the study of the mammalian central nervous system. Sci Rep 6: 26317. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26317.
- Hillman, E. M. C., Voleti, V., Li, W., and Yu, H. (2019). Light-sheet microscopy in Neuroscience. Annual Review of Neuroscience 42(1): 295–313. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-070918-050357.
- Nwaneshiudu, A., Kuschal, C., Sakamoto, F. H., Rox Anderson, R., Schwarzenberger, K., and Young, R. C. (2012). Introduction to confocal microscopy. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 132(12): 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.429.
- Briggman, K. L. and Denk, W. (2006). Towards neural circuit reconstruction with volume electron microscopy techniques. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 16(5): 562–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2006.08.010.
- Micheva, K. D. and Smith, S. J. (2007). Array tomography: A new tool for imaging the molecular architecture and ultrastructure of neural circuits. Neuron 55(1): 25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.014.
- Dodt, H.-U., Leischner, U., Schierloh, A., Jährling, N., Mauch, C. P., Deininger, K., Deussing, J. M., Eder, M., Zieglgänsberger, W., and Becker, K. (2007). Ultramicroscopy: Three-dimensional visualization of neuronal networks in the whole mouse brain. Nature Methods 4(4): 331–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1036.
- Ueda, H.R., Ertürk, A., Chung, K., et al. (2020).Tissue clearing and its applications in neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 21: 61–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-019-0250-1.
- Matryba, P., Kaczmarek, L., and Gołąb, J. (2019). Advances in ex situ tissue optical clearing. Laser and Photonics Reviews 13(8): 1800292. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201800292.
- Richardson, D. S. and Lichtman, J. W. (2015). Clarifying tissue clearing. Cell 162(2): 246–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.067.
- Molbay, M., Kolabas, Z. I., Todorov, M. I., Ohn, T.-L., and Ertürk, A. (2021). A guidebook for disco tissue clearing. Molecular Systems Biology 17(3). https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20209807.
- Wang, P., Zhang, D., Bai, S., Tao, B., Li, S., Wang, T., and Shang, A. (2020). Feasibility of commonly used fluorescent dyes and viral tracers in aqueous and solvent-based tissue clearing. Neuroscience Letters 737: 135301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135301.
- Chung, K. and Deisseroth, K. (2013). Clarity for mapping the nervous system. Nature Methods 10(6): 508–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2481.
- Kromm, D., Thumberger, T., and Wittbrodt, J. (2016). An eye on light sheet microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 133: 105-23. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Feb 27. PMID: 27263410.
- Chung. K., Wallace, J., Kim, S. Y., Kalyanasundaram, S., Andalman, A. S., Davidson, T. J., Mirzabekov, J. J., Zalocusky, K. A., Mattis, J., Denisin, A. K., Pak, S., Bernstein, H., Ramakrishnan, C., Grosenick, L., Gradinaru, V., and Deisseroth, K. (2013). Structural and molecular interrogation of intact biological systems. Nature 497(7449): 332-37. doi: 10.1038/nature12107. Epub 2013 Apr 10. PMID: 23575631; PMCID: PMC4092167.
- Hörl, D., Rojas Rusak, F., Preusser, F., Tillberg, P., Randel, N., Chhetri, R. K., Cardona, A., Keller, P. J., Harz, H., Leonhardt, H., Treier, M., and Preibisch, S. (2019).BigStitcher: Reconstructing high-resolution image datasets of cleared and expanded samples. Nat Methods 16(9): 870-74. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0501-0. Epub 2019 Aug 5. PMID: 31384047.
Authors
Jürgen Mayer, Dane Maxfield, Felix Weltzien, Malte Wachsmuth, and Savana Lipps (Luxendo-Bruker).
©2022 Bruker Corporation. MuVi SPIM is a trademark of Bruker.All other trademarks are the property of their respective companies. All rights reserved. AN2005 Rev. A0.