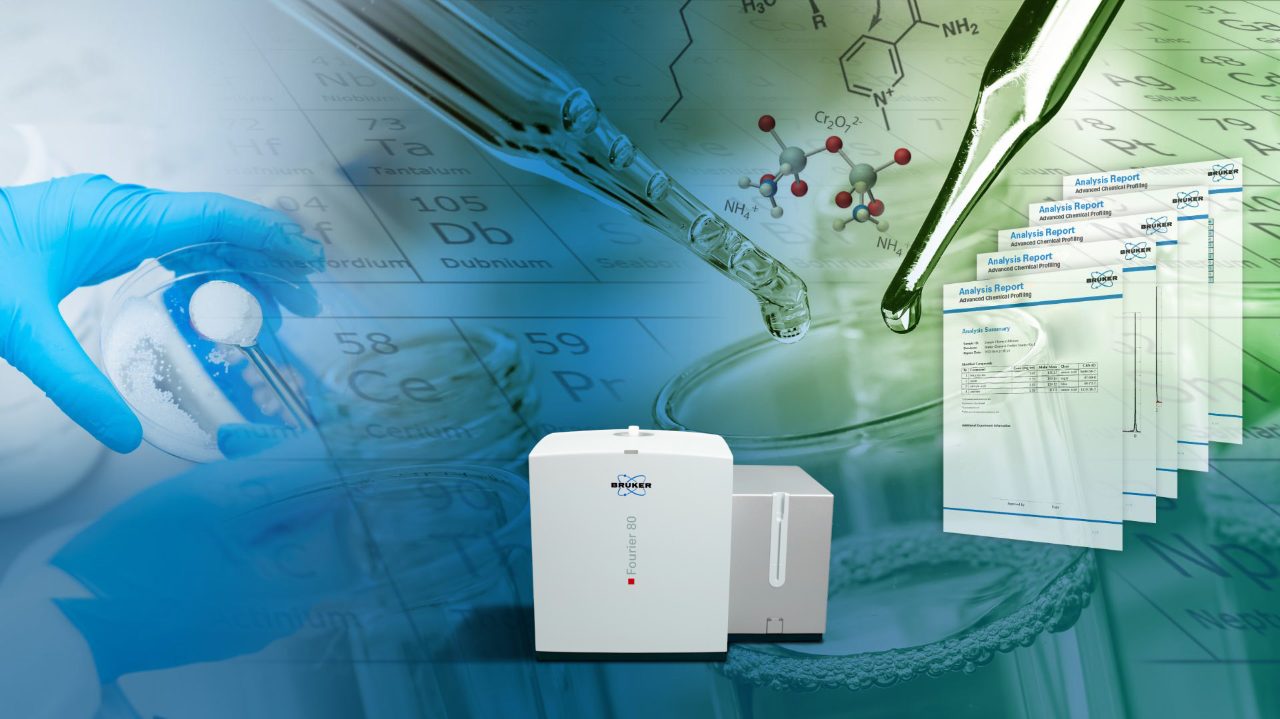
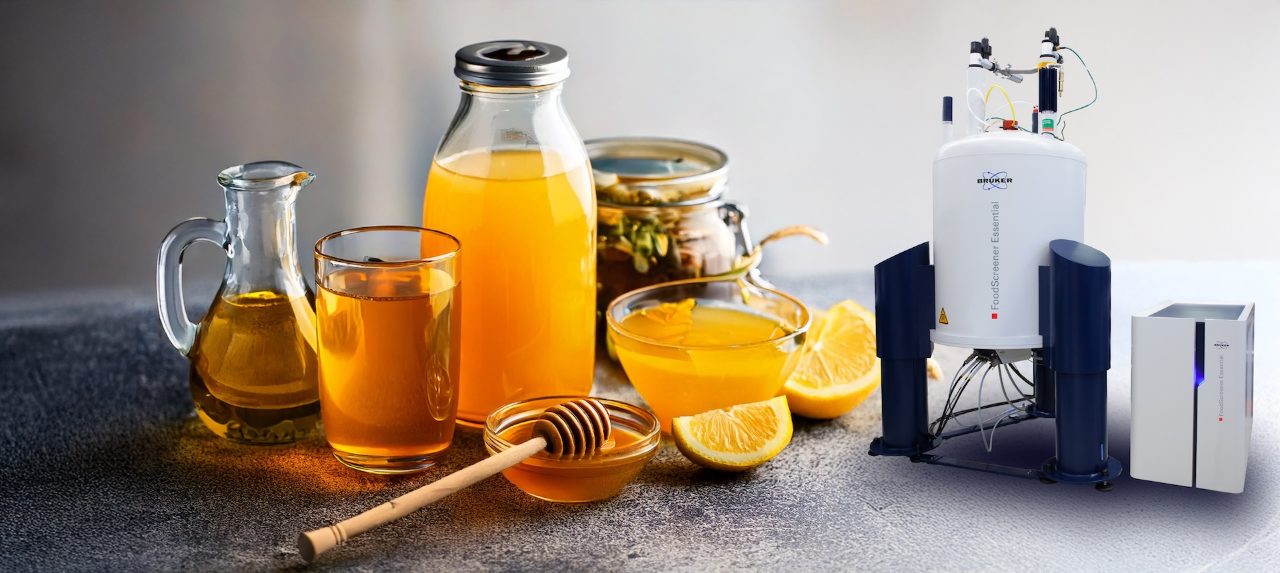
Advanced Chemical Profiling:
Automated Identification and Quantification
Comprehensive hands-off automation from physical sample to digital report
seamlessly integrated into the standard NMR instrument control software
Highlights
The solution at a glance, watch the video:
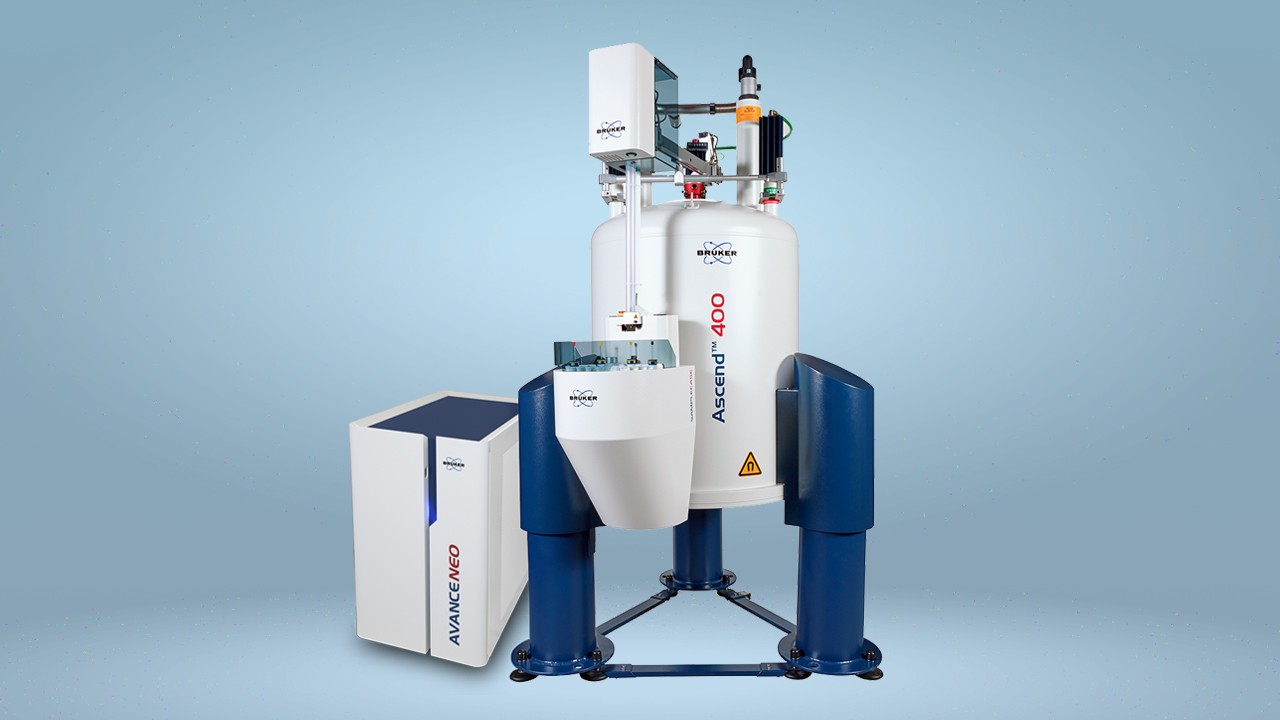
Advanced Chemical Profiling : One Integrated Solution Covering 80 to 800 MHz NMR
Our new NMR-based Advanced Chemical Profiling Software offers a truly automated, end-to-end workflow from sample to actionable information, eliminating the need for hands-on spectroscopist intervention.
Advanced Chemical Profiling processes, and interprets NMR data and files conclusive reports. It is easily applicable to substances in pure form or mixtures allowing identification and quantification of constituents in incoming goods, process intermediates, and final product formulations. The comprehensive workflow automation enhances process efficiency and quality in R&D lab-scale, pilot, and volume production processes.
The database-driven solution allows in-house NMR experts to create and implement new testing methods directly in non-NMR-expert production environments. The software automation achieves increased result consistency and comparability with operator-independent report generation.
The completely automated but tailored workflows add significant value to high-throughput environments such as production-linked labs, analytical testing services, R&D centers, and pilot-upscaling support functions within centers of excellence.
Advanced Chemical Profiling
- Free-of-charge software and tutorial video download
- Installation into TopspinTM without administrator privileges
- Free of charge database and method creation
- Ask us for a free of charge demo licence to run your first analysis
Discover Tutorials
- Database setup
- Creating reference standard
- Calibrations with external standards
- Method setup
- Analysing mixture with ACP
- Reports and interacting figures
- Users experience show case
Features
- State-of-the-art automation software for identifying and quantifying substances in pure form or mixtures.
- Seamless integration with TopSpinTM, IconNMRTM, and GoScan for comprehensive automated workflows from sample to report.
- New benchmark-setting external and internal NMR reference management feature.
- Analytical methods executable by non-NMR-Experts with a single button press.
- Operator-independent high-throughput testing for optimized result comparability and lab-to-lab method harmonization.
- Best-in-class method creation tool with intuitive operation for exceptional ease of use.
- Full on-premise installation ensuring IP security and method ownership.
Advanced Chemical Profiling Workflow
Testimonials
dsm-firmenich Science & Research
At dsm-firmenich, we’re at the forefront of innovation in nutrition, health, and beauty. We create sustainable solutions that impact our daily lives. Our cutting-edge approaches drive progress, with one area of focus being the development of novel bioprocesses.
In our R&D lab, we regularly use Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) to screen new fermentation processes. These advanced bioprocesses involve complex mixtures of media components and metabolites. Our goal is to gain an in-depth understanding and enable data-based development of new procedures.
Through our long-standing partnership with Bruker, we have been testing the latest software release from their Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution. This supports the development of the kinds of analytical workflows we use, seamlessly integrating data acquisition, processing, interpretation, and report filing. It streamlines analytical workflows and makes it easier to compare results.
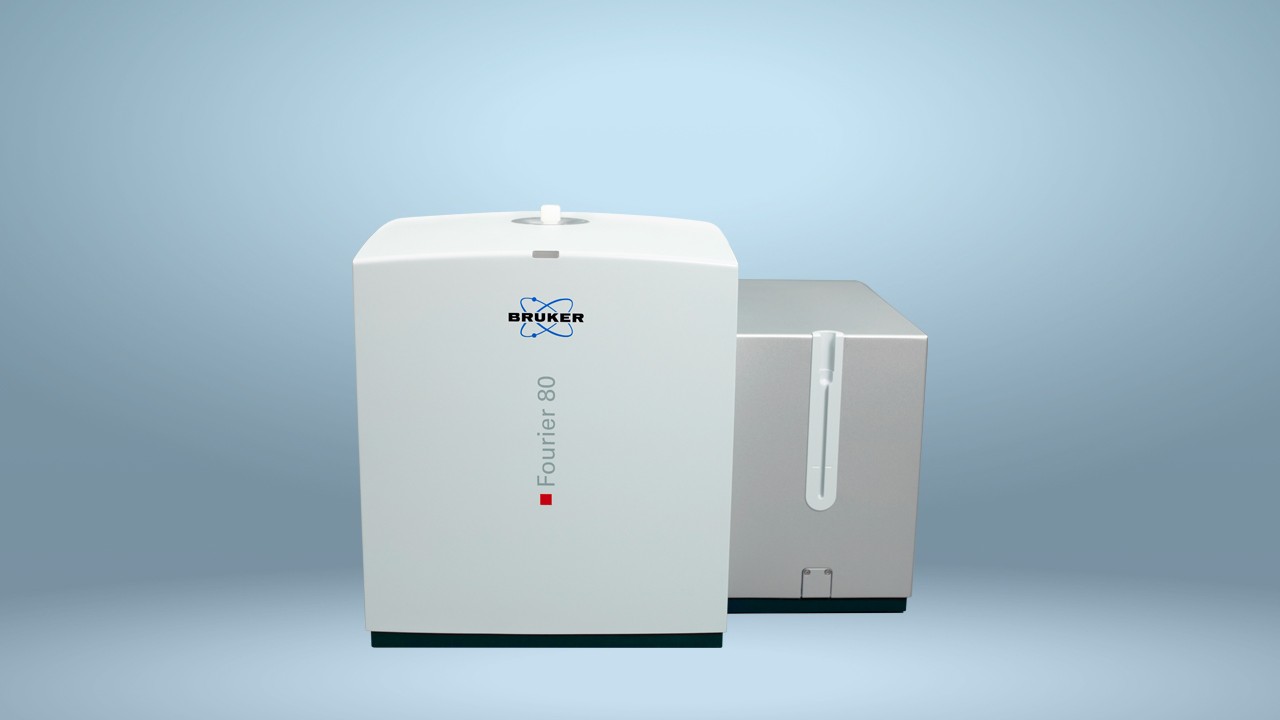
Bruker’s software platforms can be used to support scale-up from development to manufacturing. As new production routes are rolled out into manufacturing, process monitoring with a benchtop NMR system would be feasible. Bruker’s Fourier 80 benchtop system, equipped with the same Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution, could support process control in production labs.
An integrated NMR methodology - combining high-field NMR in R&D labs with benchtop systems in manufacturing - opens exciting opportunities for the industry. End-to-end use of Bruker’s solutions can make it easier to develop efficient, scalable processes.
Dr. Matthias Abele, Head of EHSQ & Sustainability, Evonik
Bruker’s new Advanced Chemical Profiling software can significantly enhance the mixture analysis process due to its robust and accurate identification and quantification feature. The complete integration into the instrument control software TopSpin and the sample automation software IconNMR™ allows for comprehensive workflow creation from the sample in the queue till the analysis report. Various concentration units and intuitive internal and external reference management makes the new software suitable for many existing analytical workflows. Once the individual methods are validated and implemented into the automated workflow, the push-button operation and operator-independent data interpretation matches industrial product quality control requirements.
Case study - WACKER is driving research in the field
of industrial carbon capture and utilization
The Avance Chemical Profiling Module helps to generate robust, reproducible quantifications of the measured data. As soon as a database is set up accordingly, the process of using the new software module does not require NMR expert knowledge. This procedure should be well suited for production environments where the contents of the samples are comparable and the sample matrices are not too complex.
Unlocking NMR Potential: Elevating NMR Beyond Structural Elucidation
R&D Lab - Structure Elucidation
Your Everyday NMR Challenge:
- Structure elucidation by NMR
- Special analytical escalation cases
- Analytical questions beyond other techniques
The Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution will support you
- Expand your portfolio with identification and quantification services
- Provide services to neighboring departments at no extra cost
- Use unused nighttime measurement slots for fully automated analysis without manual data interpretation or report filing
- Enhance NMR relevance within your organization and justify investments with multi-purpose NMR applications
R&D Lab - Process Screening
Your Everyday NMR Challenge:
- Screening of formulations, reactions, synthesis output
- Monitoring of media, intermediates, raw materials, stock solutions
- Defining and qualifying methods for validation roll-out into manufacturing (pilot or volume)
The Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution will support you
- Enhance statistical data interpretation with increased automated throughput
- Ensure highly trained experts focus on valuable tasks only
- Achieve more comparable results with operator-independent report generation
- Implement expert-developed R&D testing methods directly in non-NMR-expert production environmentsShare spectral databases and methods across your entire organization
NMR-based Analytical Services
Your Everyday NMR Challenge
- Analyzing samples of internal or external customers
- Implement tailored methods consistently
- File and submit analysis reports
The Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution will support you
- Boost throughput with automated sample-to-report routines
- Develop diverse methods for various use-cases
- Standardize and harmonize testing methods for all customers
- Automate professional report generation for direct submission
- Reduce time-to-result for enhanced customer satisfaction
- Scale to new business opportunities without additional costs
QC Lab @ Manufacturing
Your Everyday NMR Challenge
- Quality control testing of products
- Screening and control of incoming goods
- Analyzing process intermediates
- Troubleshooting and failure analysis
The Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution will support you
- Boost throughput with automated sample-to-report routines
- Achieve operator-independent results in multi-shift environments
- Standardize and harmonize testing methods across the entire value chain
- Reduce time-to-result with automated batch-release testing
- Scale to different product lines without additional costs
- Enhance IP security with on-premise installation
Forensic Narcotics Testing
Your Everyday NMR Challenge
- Analyzing narcotics samples
- Identifying and quantifying suspicious substances
- Detecting New Psycoactive Substances (NPS)
- Filing and submitting reports for legal proceedings
The Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution will support you
- Identify narcotics, cutting agents and fillers through automatic database matching
- Hit the ground running with free-of-charge narcotics and fillers database
- Share database with your forensic network in a Distributed Lab Topology
- Quantify constituents of confiscated samples
- Detect unknown compounds / NPS
- Automate professional report generation for documentation and legal proceedings
Are you living in a Distributed Lab Topology Environment?
Globally organized companies might request from their labs these duties
- Method developed on R&D High-Resolution (HiRes) NMR systems
- Pilot manufacturing support by R&D department
- Volume manufacturing method development for non-expert operation (QC)
- QC method validation via R&D method
The Advanced Chemical Profiling Solution will support you in:
- Direct HiRes NMR method roll-out to QC if needed
- HiRes NMR to benchtop NMR method translation if possible
- Direct (HiRes/HiRes) or In-Tech (HiRes/Benchtop) method validation decreases time-to-market
- Database-driven method scaling opportunity to other product lines (same instrument possible)
Download Distributed Lab Topology eBook: