Acquifer IM
Acquifer IM
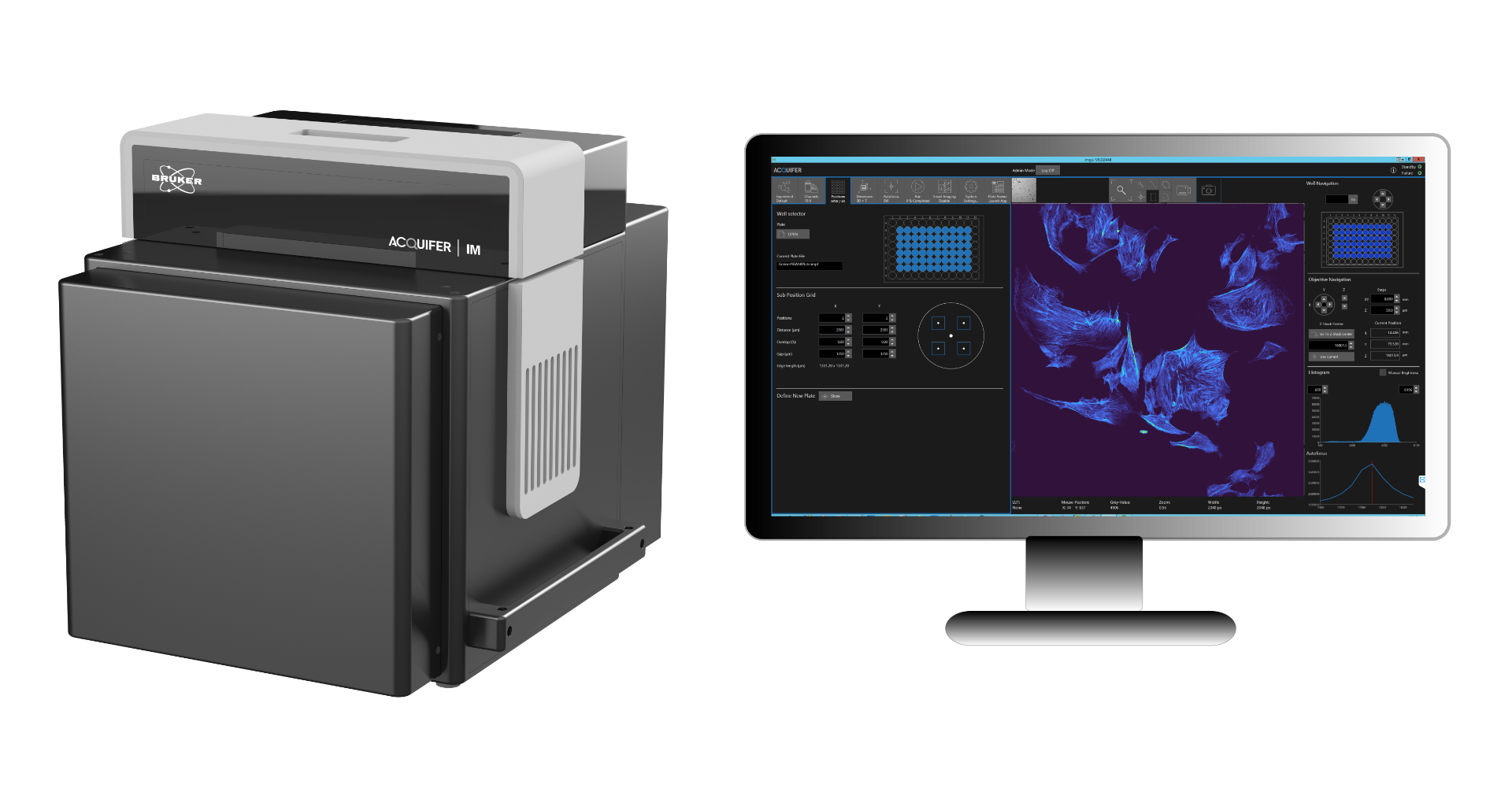
Acquifer IM (Imaging Machine) is a fully automated widefield microscope with data storage and processing capabilities ideal for high-content screening assays and phenotypic screening for small-model organisms. Its static sample holder with a mobile optical unit ensures sample stability during imaging, making it ideal for imaging motion-sensitive samples, such as non-adherent cell cultures or embryos.
High-Content Screening
The Acquifer IM is a high-performance solution for screening and high-throughput imaging assays and is compatible with all commonly available multi-well plates (adaptions possible). A host of unique features include built-in temperature regulation, a robotic lid, and an open interface for seamless integration into automated workflows. Its comprehensive data storage and processing integrations are ideal for researchers performing high-content or phenotypic screening.
The software and workflow enable low-magnification pre-screen data of a full microtiter plate to be readily visualized in the Plate-Viewer software on the Acquifer IM high-throughput screening microscope. Different tools and matching algorithms enable the selection of regions of interest (ROIs) for each well and robust autolocalization of target structures for feedback microscopy.
Acquifer IM is optimized for your high-throughput experiments with:
- Optimal imaging conditions for sensitive specimens and long-term observations
- Uniblock optical design moves to your sample while your sample remains stationary
- Built-in temperature control (20 to 40°C) ± 0.5°C homogeneity over whole plate and over time
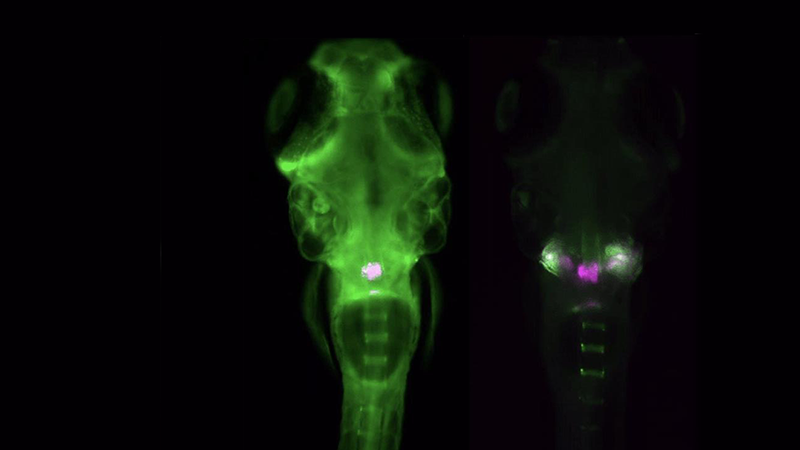
Zebrafish Imaging
The Acquifer IM is ideally suited for high-throughput screening of zebrafish, an important preclinical model to study development, disease, and molecular and drug screening. The combination of a static sample holder, a mobile optical unit, and built-in temperature regulation ensures specimen stability during imaging.
Organoid Imaging
Acquifer IM provides invaluable insights into cellular structures and dynamic processes, such as tissue morphogenesis, differentiation, and biophysics. With the ability to conduct high-throughput screenings, it supports the study of developing organoids in combination with advanced genome editing techniques and tissue sections.
Other Applications
Specifications
| Objective | Magnification | Numerical Aperture | Working Distance |
| CFI P-Achromat UW2X | 2x | 0.06 | 7.5 |
| CFI Plan Fluor4X | 4x | 0.13 | 17.2 |
| CFI Plan Fluor10X | 10x | 0.3 | 16.0 |
| CFI S P-Fluor ELWD20xC | 20x | 0.45 | 8.2-6.9 |
| CFI S P-Fluor ELWD40xC | 40x | 0.6 | 3.6-2.8 |
IM Dimensions: 553mm (21.77") H x 528mm (20.79") W x 555mm (21.85") D
Photomanipulation
The photomanipulation module was developed in collaboration with Rapp Optoelectronic, Wedel, Germany, who has over 20 years of experience in high-performance photomanipulation and advanced light microscopy techniques.
Its robust design enables researchers to perform advanced experiments with ease. Full datasets of entire microplates can be annotated and subsequently automatically photomanipulated without further user interaction. This enables large scale photomanipulation for various biomedical assays.
The module is an optional hardware upgrade allowing researchers to easily scale-up complex photomanipulation experiments such as photodamaging of cells and tissues, switch convertible fluorophores, uncage compounds or perform optogenetic activation.
The Plate-Viewer Software on the Acquifer IM High-Throughput Screening Microscope
The Plate-Viewer visualization software utilizes data acquired with the Acquifer IM high-throughput screening microscope. The user interface and design allow for intuitive working with datasets, such as overviews of screening data, inspection of individual images and functionalities to adjust channels-display, save data visualizations or time-lapse movies.
Both the system and Plate-Viewer have an open interface that enables automated workflows and feedback-microscopy functionalities.
- Conversion and export of images: Export of single z-planes, z-projections, z-stacks or time-series allows for versatility in data analysis. Also, batch export and various file formats (tif, jpeg, png, bmp, mp4) are available.
- Feedback Microscopy: Features, such as automated object-detection algorithm and pre-scan ROI-selection enable feedback microscopy.
- Plugin Interface: Data processing with external software utilizes a plugin interface. Advanced users can generate their own plugins.
Publications
| Year | Journal | Title | Author(s) | Subject | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | Heidelberg Thesis | Modeling human PMM2-CDG in medaka to understand systemic effects of hypoglycosylation on development | Pakari Kaisa | congenital disorders of glycosylation, PMM2 deficiency, protein hypoglycosylation, embryonic development, medaka | precision genome editing, base editing, conditional protein degradation, translational disease modelling, quantitative proteomics |
| 2026 | BioRvix preprint | Glomerular Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Cross the Basement Membrane to Regulate Podocyte Function | Janina Kern, Sindhu Thiagarajan, Nina Sopel, Alexandra Ohs, Patricia Luckner, Astrid Bruckmann, Jan Van Deun, Mustafa Kocademir, George Sarau, Silke Christiansen, Christoph Daniel, Mario Schiffer, Stefan Uderhardt, Janina Müller-Deile | glomerular endothelial cell, podocyte, vesicle | nanoparticle tracking analysis, electron microscopy, RAMAN spectroscopy and flow cytometry. |
| 2025 | Heidelberg Thesis | Organoid-based studies on the fundamental rules of retinal tissue self-organization and patterning | Schlagheck Christina Maria | retinal development, organoids, mechanical patterning, cell fate specification, medaka | retinal organoid culture, biomechanical manipulation, 3D stem cell models, extracellular matrix supplementation, developmental pattern analysis |
| 2025 | Heidelberg Thesis | Understanding and modulating molecular mechanisms of peritoneal transport function to improve peritoneal dialysis efficacy and outcome | Iva Marinovic | peritoneal dialysis, peritoneal mesothelium, solute transport, tight junctions, chronic kidney disease | RNA sequencing, in vitro barrier models, immunocytochemistry, single-molecule localisation microscopy, functional transport assays |
| 2025 | BioRvix preprint | Discovery and characterisation of gene by environment and epistatic genetic effects in a vertebrate model | Bettina Welz, Saul Pierotti, Tomas Fitzgerald, Thomas Thumberger, Risa Suzuki, Philip Watson, Jana Fuss, Tiago Cordeiro da Trindade, Fanny Defranoux, Marcio Ferreira, Kiyoshi Naruse, Felix Loosli, Jakob Gierten, Joachim Wittbrodt, Ewan Birney | phenotypic plasticity, heart rate regulation, complex traits, gene–environment interaction, medaka | QTL mapping, F2 segregation analysis, interaction modelling, gene editing, GWAS power simulation |
| 2025 | Heidelberg Thesis | Design and implementation of workflow tools for multiplexed time-lapse imaging experiments in zebrafish screening | Satheesan Sankeert | zebrafish-based screening, multiplexed time-lapse imaging | zebrafish, sample preparation, workflow, image analysis |
| 2025 | Zeitschrift für Geburtshilfe und Neonatologie | Automatisierte Laserablation in der Zebrafischlarve als High-Content Modell für die akute Nierenschädigung und epigenetisches Drug-Screening auf regenerationsmodulierende Substanzen | L. Rapp, et al. | Acute kidney injury (AKI), regeneration | Laser ablation in zebrafish larvae, epigenetic drug screening |
| 2024 | MicroPublication Biology | Virtual Orientation Tools (VOTj): Fiji plugins for object centering and alignment | S. Satheesan, J. Gehrig, LSV. Thomas | Sample alignment and orientation | Fiji plugin for centering and aligning biological objects |
| 2023 | Biospektrum | In vivo-Medikamenten-Screening zur Behandlung von Glomerulopathien | M. Schindler, S.M. Bach, J. Gehrig, et al. | Glomerulopathies | In vivo drug screening in zebrafish models |
| 2023 | Journal of the American Society of Nephrology | A Novel High‑Content Screening Assay Identified Belinostat as Protective in a Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis–like Zebrafish Model | S. Maximilian Schindler, Florian Siegerist, Tim Lange, Sandra Simm, Sofia M. Bach, Matthias Klawitter, … Nicole Endlich | Embryonic/fetal kidney (FSGS-like) | High-content screening in zebrafish embryos |
| 2023 | Sci Rep | Identification of side effects of COVID‑19 drug candidates on embryogenesis using an integrated zebrafish screening platform | A. Ernst, I. Piragyte, A. M. MP, N. D. Le, D. Grandgirard, S. Leib, … N. Mercader | Embryogenesis, teratogenicity | Integrated in vivo zebrafish screening |
| 2023 | Nat. Methods | EmbryoNet: using deep learning to link embryonic phenotypes to signaling pathways | D. Čapek, M. Safroshkin, H. Morales‑Navarrete, N. Toulany, G. Arutyunov, A. Kurzbach, … P. Müller | Embryonic development: phenotype–pathway mapping | Deep‑learning phenotyping (EmbryoNet) |
| 2023 | Front. Cell Dev. Biol. | pyHeart4Fish: Chamber‑specific heart phenotype quantification of zebrafish in high‑content screens | V. L. Vedder, T. Reinberger, S. M. Haider, L. Eichelmann, N. Odenthal, S. Abdelilah‑Seyfried, … J. Erdmann | Cardiac chamber morphology/function | High-content imaging + python-based phenotyping |
| 2022 | Front. Cell Dev. Biol. | The shGlomAssay combines high‑throughput drug screening with downstream analyses and reveals the protective role of Vitamin D3 and Calcipotriol on podocytes | M. C. Ristov, T. Lange, N. Artelt, N. Nath, A. W. Kuss, J. Gehrig, … N. Endlich | Glomerular podocytes, nephrotoxicity | High-throughput drug screening in zebrafish kidney model |
| 2022 | eLife | Boosting targeted genome editing using the hei‑tag | T. Thumberger, T. Tavhelidse‑Suck, J. A. Gutierrez‑Triana, A. Cornean, R. Medert, B. Welz, … J. Wittbrodt | Genome editing (CRISPR enhancement) | in vivo zebrafish genome editing using hei‑tag |
| 2021 | JASN | Glomerular Endothelial Cell‑Derived microRNA‑192 Regulates Nephronectin Expression in Idiopathic Membranous Glomerulonephritis | J. Müller‑Deile, N. Sopel, A. Ohs, V. Rose, M. Gröner, C. Wrede, … M. Schiffer | Glomerular endothelial signaling | Molecular biology, in vivo glomerular analysis |
| 2020 | Cells | A Multiparametric Assay Platform for Simultaneous In Vivo Assessment of Pronephric Morphology, Renal Function and Heart Rate in Larval Zebrafish | P. J. Steenbergen, J. Heigwer, G. Pandey, B. Tönshoff, J. Gehrig, J. H. Westhoff | Kidney morphology/function + cardiac physiology | Multiparametric live zebrafish screening |
| 2019 | Int. J. Mol. Sci. | A smart imaging workflow for organ‑specific screening in a cystic kidney zebrafish disease model | G. Pandey, J. H. Westhoff, F. Schaefer, J. Gehrig | Cystic kidney disease | Automated organ‑specific imaging |
| 2014 | BMC Biotech | Generation of orientation tools for automated zebrafish screening assays using desktop 3D printing | J. N. Wittbrodt, U. Liebel, J. Gehrig | Zebrafish embryo orientation |