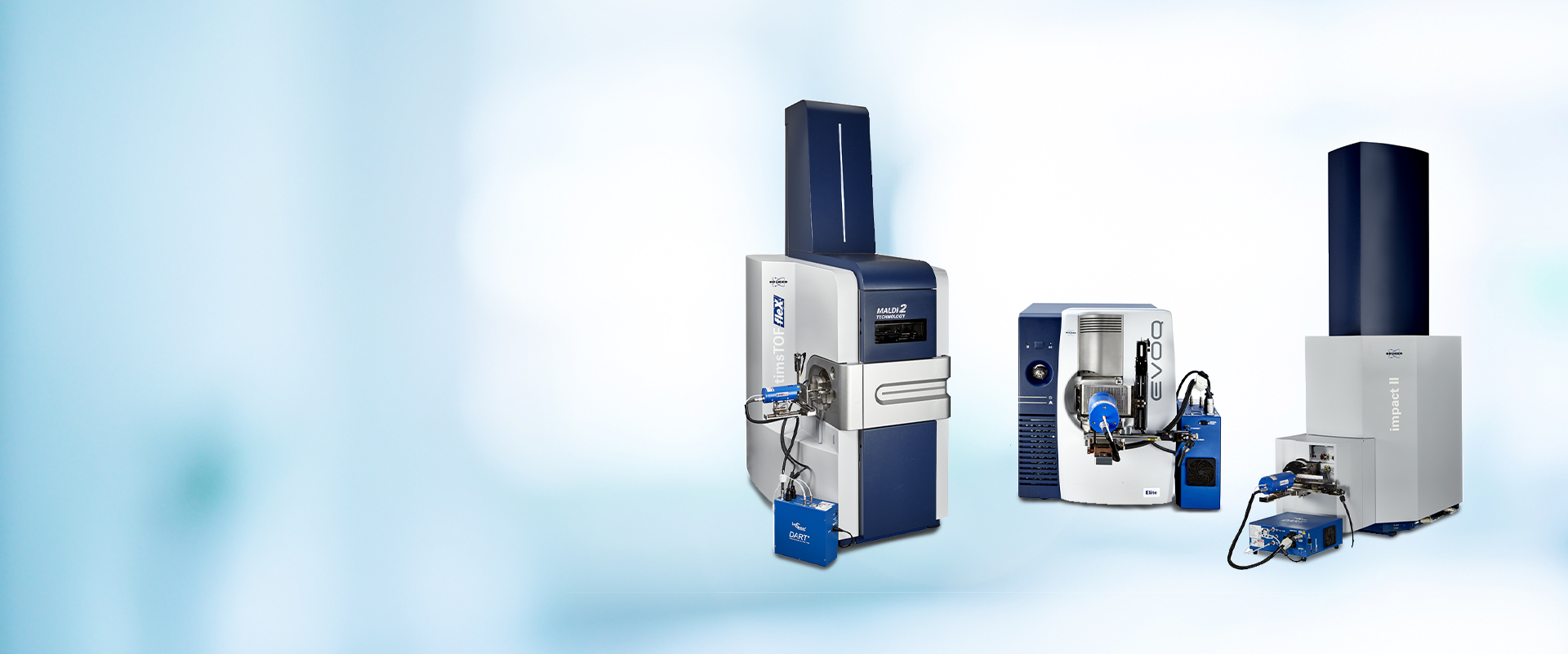
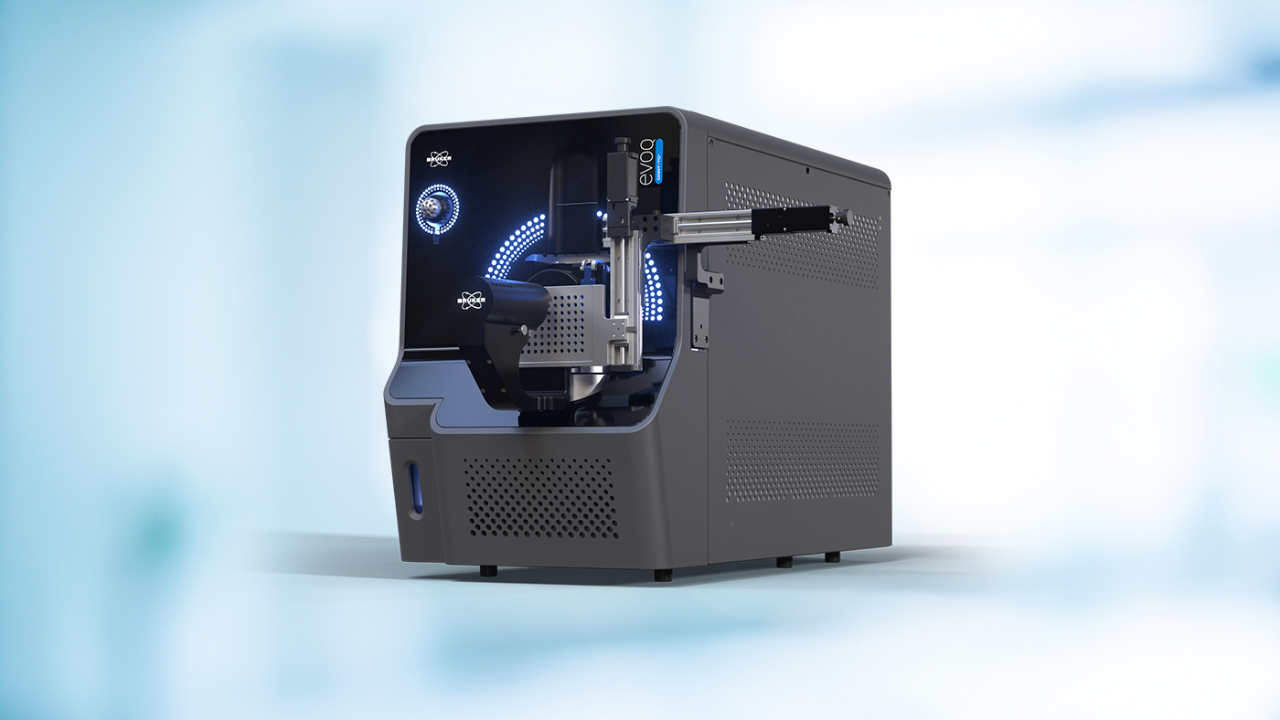
DART-MS: Direct Analysis in Real Time Mass Spectrometry
Analyze More, Faster with DART-MS
DART-MS (Direct Analysis in Real Time Mass Spectrometry) is a powerful ionization technology enabling rapid, versatile analysis across solids, liquids, and gases - all in their native forms.
Whether in the lab or the field, DART-MS empowers users to conduct high-throughput analyses on surfaces as diverse as concrete, human skin, and currency, making it ideal for fast, actionable insights.
Why Choose DART-MS?
DART-MS enables seamless integration with existing mass spectrometers, allowing you to add versatility to your workflows. With ambient ionization and high-throughput capabilities, DART-MS makes it easy to detect chemicals in seconds on varied surfaces like concrete, human skin, and food packaging.
Key Advantages of DART-MS:
- Chromatography-Free: No complex sample prep allows faster analysis than GC-MS or LC-MS.
- Increased Throughput: Process up to 1,500 samples per day.
- Cost-Effective and Eco-Friendly: Reduced consumables, fewer chemicals, and minimal waste —making labs greener and more cost-effective.
How DART Works
DART-MS relies on a gas-phase ionization method where an inert gas (helium, nitrogen) generates excited-state species in a plasma stream. This heated stream ionizes analytes near the mass spectrometer inlet, enabling real-time detection without chromatography.
Features:
- Corona Discharge Plasma: Creates excited atoms and molecules that initiate ionization.
- Temperature Control: A heater coil adjusts gas temperature, enhancing desorption of sample molecules.
- Ion Suppression Grid: Prevents recombination, ensuring high ion availability for reliable analysis.
Seamless Integration with Bruker HyStar Plug-In for DART
Bruker’s HyStar Plug-in allows DART-MS to integrate effortlessly into the existing Bruker ecosystem. With this integration, users can develop methods, log data, and manage workflows in a unified software interface, transforming DART-MS into a fully connected analytical solutionC.
Direct Ionization Techniques for Mass Spectrometry
Direct ionization methods like DART-MS, Laser Diode Thermal Desorption (LDTD), and PaperSpray are revolutionizing mass spectrometry with fast, chromatography-free analysis.
DART-MS stands out as the top choice for direct ionization mass spectrometry. Its key advantages include minimal sample preparation, high sensitivity, and rapid analysis times, making it ideal for forensic analysis, drug testing, food safety, and environmental monitoring applications. DART-MS is the most efficient and versatile method for direct ionization, delivering consistent performance across diverse sample matrices with minimal consumable costs.
See why DART-MS is the preferred choice for high-throughput, accurate results.
| Characteristic | DART-MS | LDTD | PaperSpray |
| Ionization Source | Heated gas stream ionization: DART-OS, DART JumpShot, DART JumpShot HTS | Laser diode-induced desorption | Electrospray ionization from paper |
| Sample Type | Solid, Liquid, Gas, Powder | Liquid (extracted solids) | Liquid (extracted solids) |
| Sample Preparation | Minimal or no preparation | Requires drying and matrix addition | Requires solvent application, can be inconsistent |
| Analysis Speed | Ultra-fast (seconds per sample); 15 mins for 96-384 samples | Fast, but needs plate cooling (0.9-18 secs/sample) | Moderate (1-2 mins/sample); 8 hrs for 240 samples |
| Consumable Costs | Low (requires minimal materials) | High (plates and matrix additives) | Moderate (disposable paper cartridges) |
| Sample Throughput | High (efficient 96-384 sample analysis) | High throughput, limited by plate cooling | Lower (slower due to solvent handling) |
| Analyte Compatibility | Broad (volatile, semi-volatile, non-volatile) | Primarily semi-volatile and volatile | Limited to polar/semi-polar compounds |
| Matrix Effects | Low (direct ambient ionization) | High (matrix interference possible) | High (ion suppression from matrix) |
| Quantitative Analysis | High accuracy and reproducibility; qualitative and semi-quantitative | Good with complex matrix but requires optimization | Moderate; influenced by paper/solvent choice |
| Instrument Complexity | Low (simple setup) | Moderate (laser calibration needed) | High (requires specific paper handling techniques) |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low (few consumable changes) | High (frequent laser/plate maintenance) | High (paper clogging, solvent contamination) |
| Environmental Impact | Low (minimal waste, no solvents) | Moderate (solvent for matrix prep) | Higher (solvents and paper waste generated) |
| Adaptability to Different Workflows | Highly adaptable (various sample forms: liquid, solid, gas) | Moderate (needs plate format) | Limited (dependent on paper and solvents) |
For Research Use Only. Not for use in clinical diagnostic procedures.